1.3.2 | CALCULATING FILE SIZE |
|
Topics from the Cambridge IGCSE (9-1) Computer Science 0984 syllabus 2023 - 2025.
|
OBJECTIVES
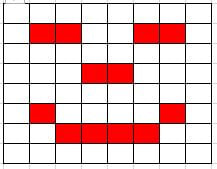
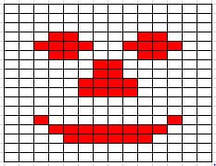
1.3.2 Calculate the file size of an image file and a sound file, using information given |
ALSO IN THIS TOPIC
1.1.1 NUMBER SYSTEMS 1.1.2 NUMBER SYSTEMS 1.1.3 NUMBER SYSTEMS 1.1.4 NUMBER SYSTEMS 1.1.5 NUMBER SYSTEMS 1.1.6 NUMBER SYSTEMS 1.2.1 TEXT, SOUND AND IMAGES 1.2.2 TEXT, SOUND AND IMAGES 1.2.3 TEXT, SOUND AND IMAGES 1.3.1 STORAGE AND COMPRESSION YOU ARE HERE | 1.3.2 STORAGE AND COMPRESSION 1.3.3 STORAGE AND COMPRESSION 1.3.4 STORAGE AND COMPRESSION TOPIC 1 KEY TERMINOLOGY TOPIC 1 ANSWERS TOPIC 1 TEACHER RESOURCES (CIE) |