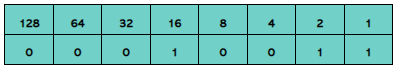
1.1.5 | BINARY SHIFT |
|
Topics from the Cambridge IGCSE (9-1) Computer Science 0984 syllabus 2023 - 2025.
|
OBJECTIVES
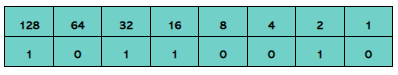
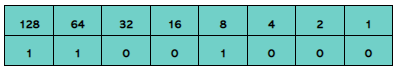
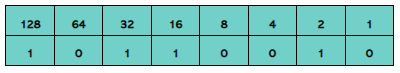
1.1.5 Perform a logical binary shift on a positive 8-bit binary integer and understand the effect this has on the positive binary integer |
ALSO IN THIS TOPIC
1.1.1 NUMBER SYSTEMS 1.1.2 NUMBER SYSTEMS 1.1.3 NUMBER SYSTEMS 1.1.4 NUMBER SYSTEMS YOU ARE HERE | 1.1.5 NUMBER SYSTEMS 1.1.6 NUMBER SYSTEMS 1.2.1 TEXT, SOUND AND IMAGES 1.2.2 TEXT, SOUND AND IMAGES 1.2.3 TEXT, SOUND AND IMAGES 1.3.1 STORAGE AND COMPRESSION 1.3.2 STORAGE AND COMPRESSION 1.3.3 STORAGE AND COMPRESSION 1.3.4 STORAGE AND COMPRESSION TOPIC 1 KEY TERMINOLOGY TOPIC 1 ANSWERS TOPIC 1 TEACHER RESOURCES (CIE) |