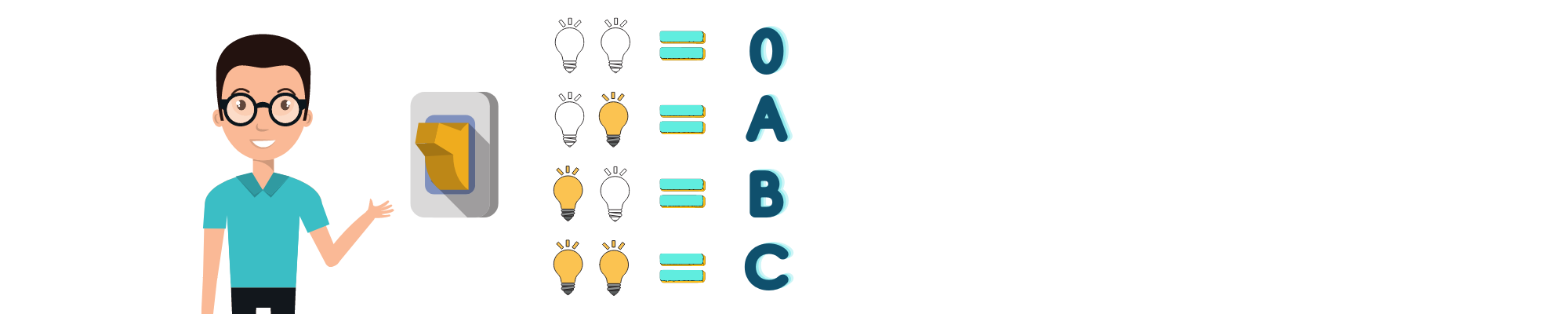DATA REPRESENTATION | WHAT IS BINARY
DESIGNED FOR CIE GCSE EXAMINATIONS
OBJECTIVES
1.1.1 Understand how and why computers use binary to represent all forms of data.
1.1.1 Understand how and why computers use binary to represent all forms of data.
- Any form of data needs to be converted to binary to be processed by a computer
- Data is processed using logic gates and stored in registers
Whilst computer are complex machines that are capable of a countless number of functions at an incomprehensible speed, when they are broken down to their most simple form, they are little more complex than a light switch. Imagine if you had just two light switches and represented a letter with each combination of the switch settings, you could represent 4 different letters.
When you press a key on your keyboard an electrical signal is sent to your computer and converted to a binary representation, a combination of switches being on or off. To make it easy for visual representation we represent the OFF state with zeros and the ON state with ones. For example, when you press the letter A on your keyboard the electrical signal is converted and stored as 01000001, the letter B is stored as 01000010.
Whilst at its core the computer is no more complicated than a light switch, when you combine billions of light switches with the hundreds of thousands of components that create your computer, impressive things can be done.
Every keystroke, pixel on your screen, image you upload, sound played by your computer is all converted to a binary representation to be stored and processed on your computer.
Every process your computer does can be broken down to its binary representation, the processor can process billions of operations per second and each binary value is stored in a very fast and very small section of memory called a register whilst it is waiting to be processed.
Whilst at its core the computer is no more complicated than a light switch, when you combine billions of light switches with the hundreds of thousands of components that create your computer, impressive things can be done.
Every keystroke, pixel on your screen, image you upload, sound played by your computer is all converted to a binary representation to be stored and processed on your computer.
Every process your computer does can be broken down to its binary representation, the processor can process billions of operations per second and each binary value is stored in a very fast and very small section of memory called a register whilst it is waiting to be processed.
QUICK QUESTION
What is Binary?
A) A number system that uses digits 0 through 9
B) A number system that uses digits 0 and 1
C) A method for representing negative numbers
D) An operation that moves bits left or right within a binary number
EXPLAINATION
The answer is B) A number system that uses digits 0 and 1 because the binary number system, also known as base-2, consists only of two digits: 0 and 1. Each digit in a binary number represents a power of 2, making it fundamental to computer systems and digital electronics.
Binary: A number system that uses only two digits, 0 and 1.
Logic Gates: Electronic circuits that perform basic logic functions such as AND, OR, and NOT.
Registers: Small, fast storage locations in a computer's CPU that hold data temporarily during processing.
Logic Gates: Electronic circuits that perform basic logic functions such as AND, OR, and NOT.
Registers: Small, fast storage locations in a computer's CPU that hold data temporarily during processing.
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1: What is the main reason why computers use binary to represent data?
A) It is the most efficient way
B) It is the easiest way
C) It is the only way
D) It is the most convenient way
2: How does binary representation of data allow computers to perform calculations and logical operations?
A) By using specific arithmetic circuits
B) By using specific logic circuits
C) By using specific memory circuits
D) By using specific input/output circuits
3: What are the limitations of using binary to represent data in computers?
A) It can only represent whole numbers
B) It is limited by memory size
C) It is limited by processing speed
D) All of the above
4: What is the relationship between binary representation of data and the hardware of a computer?
A) The hardware is designed to work with binary data
B) The hardware is limited by binary data representation
C) The hardware has no relationship with binary data representation
D) The hardware can be designed to work with data represented in other forms besides binary
A) It is the most efficient way
B) It is the easiest way
C) It is the only way
D) It is the most convenient way
2: How does binary representation of data allow computers to perform calculations and logical operations?
A) By using specific arithmetic circuits
B) By using specific logic circuits
C) By using specific memory circuits
D) By using specific input/output circuits
3: What are the limitations of using binary to represent data in computers?
A) It can only represent whole numbers
B) It is limited by memory size
C) It is limited by processing speed
D) All of the above
4: What is the relationship between binary representation of data and the hardware of a computer?
A) The hardware is designed to work with binary data
B) The hardware is limited by binary data representation
C) The hardware has no relationship with binary data representation
D) The hardware can be designed to work with data represented in other forms besides binary
OPEN ENDED QUESTIONS
- What is binary and how does it relate to computers?
- Why do computers use binary to represent data?
- Can a computer process data in any other form besides binary?
- What is the significance of logic gates in computer processing?
- How does data get converted into binary before being processed by a computer?
- What role do registers play in storing data in a computer?
- How does binary representation of data allow computers to perform calculations and logical operations?
- What are the advantages of using binary to represent data in computers?
- What are the limitations of using binary to represent data in computers?
- What is the relationship between binary representation of data and the hardware of a computer?